What is a Circle?
We can simply say that a circle is a round-shaped figure that has no corners or edges. Which is one of the famous curves in the conic section
Definition of Circle
The collection of all points that are equally distant from a single point is known as a circle. This point is known as the center of the circle. In geometry, also a circle can be defined as a closed, two-dimensional curved shape.
Euclid’s Definition
A circle is a plane figure bounded by one curved line, and such that all straight lines drawn from a certain point within it to the bounding line, are equal. The bounding line is called its circumference and the point, its center
Parts of a Circle

Chord
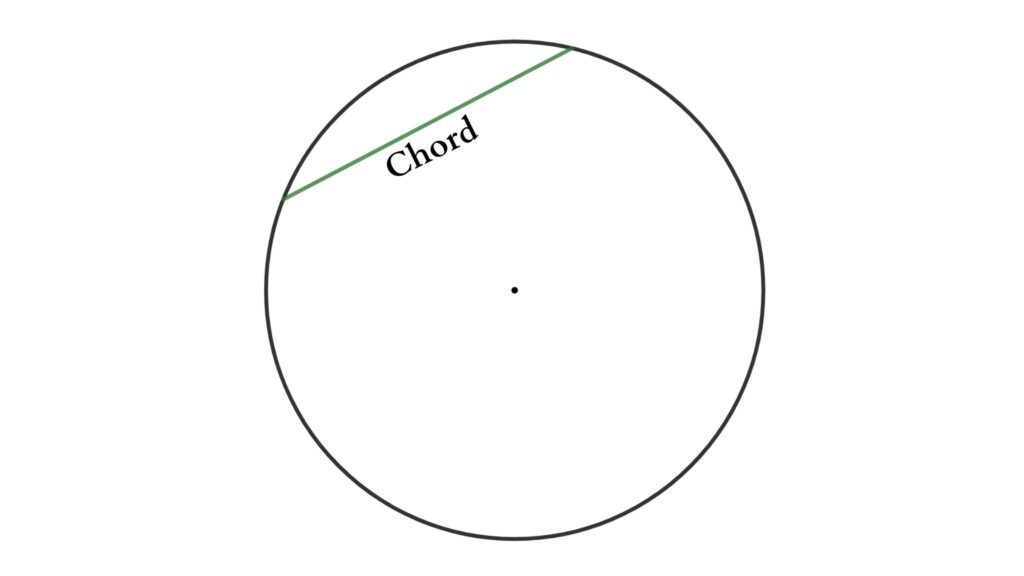
A chord is a straight line that connects the two points of a circle in geometry. When a chord passes through the center of a circle, it becomes the circle’s diameter. The diameter is the “largest” chord in the circle.
Radius

The radius is the straight line which is connecting the circle’s center to any point on the circle.
Diameter
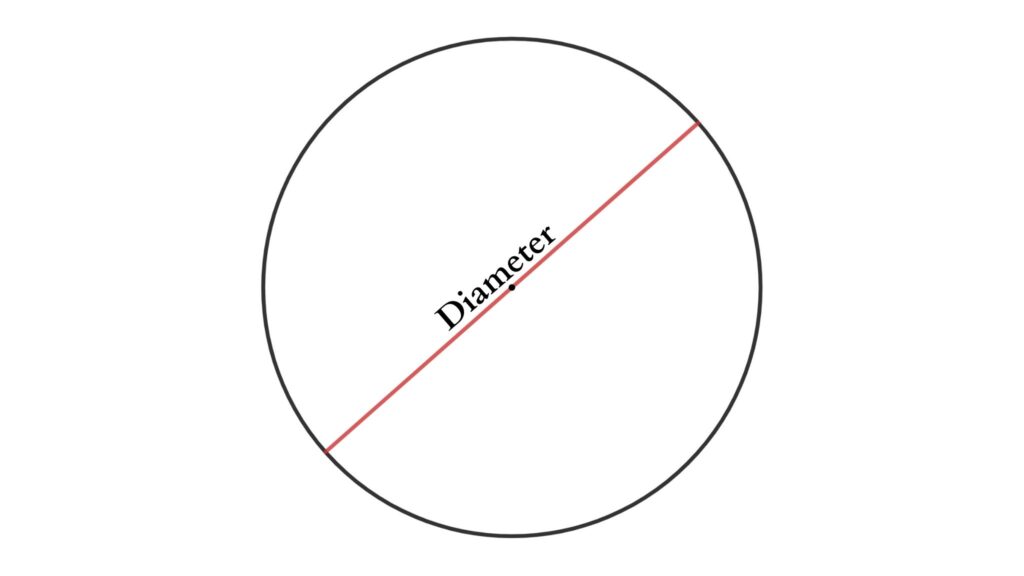
It is the distance between two points on a circle that passes through the center. The diameter is twice the length of the radius.
Secant
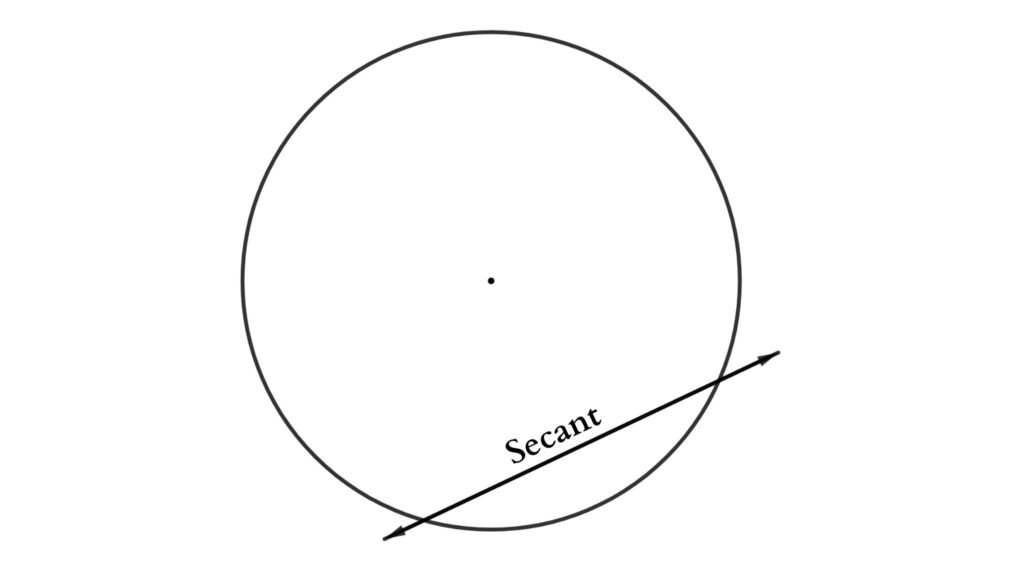
A secant is a line segment that intersects the circle twice. A chord exists in a distinct secant line, and each secant line defines a distinct chord.
Tangent
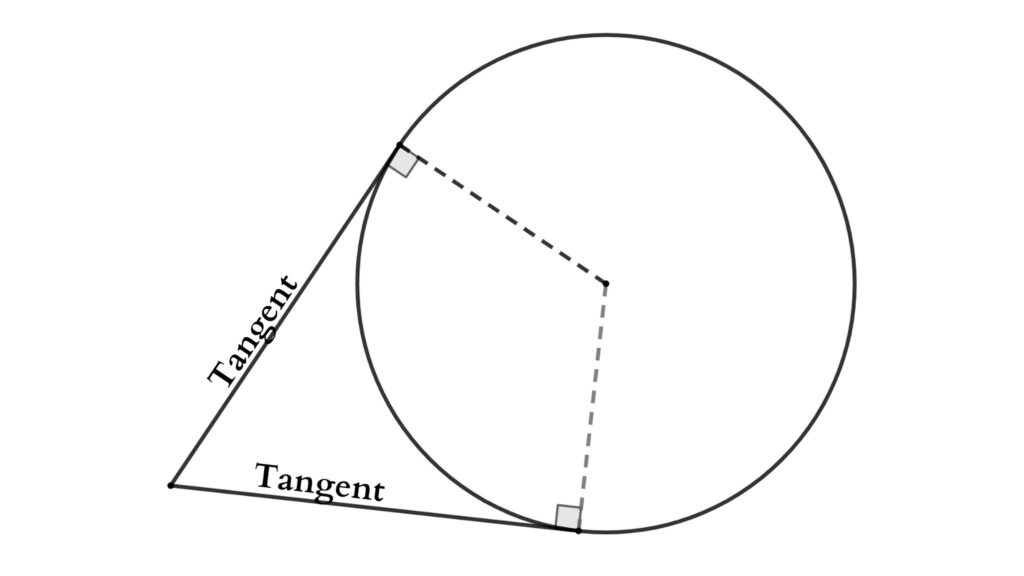
A tangent to a circle is a straight line that touches the circle only once. This is referred to as the point of tangency. A tangent is always perpendicular to the radius at the point of tangency. Tangents at the end of the diameter are parallel.
Area
The area enclosed by a circle of radius r is denoted by πr² in geometry. The Greek letter π represents the constant ratio of any circle’s circumference to its diameter, which is approximately equal to 3.1415….
Perimeter
The perimeter is calculated using the formula 2πr, where r is the radius and π is a constant. π is equal to the ratio of the circumference to the diameter (or twice the radius) which is equal to 3.1415…
Semicircle

A semicircle is formed by cutting a circle along its diameter, and its whole arc always measures 180 degrees.
Quarter Circle
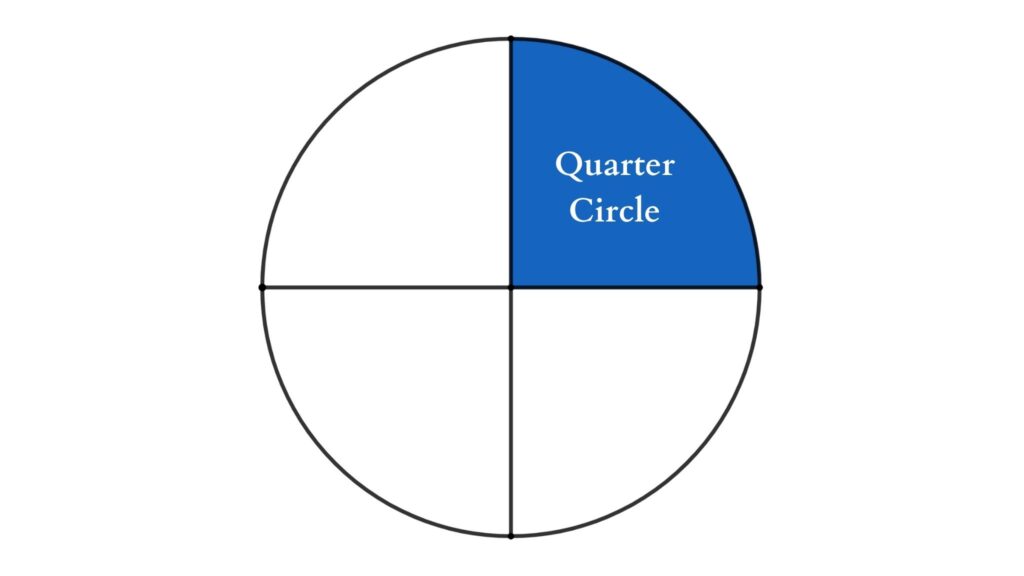
A quarter circle is formed by slicing a circle into four equal pieces through its center. One of the four pieces is represented by a quarter circle. The arc of a quarter circle will always be 90 degrees.
Sector
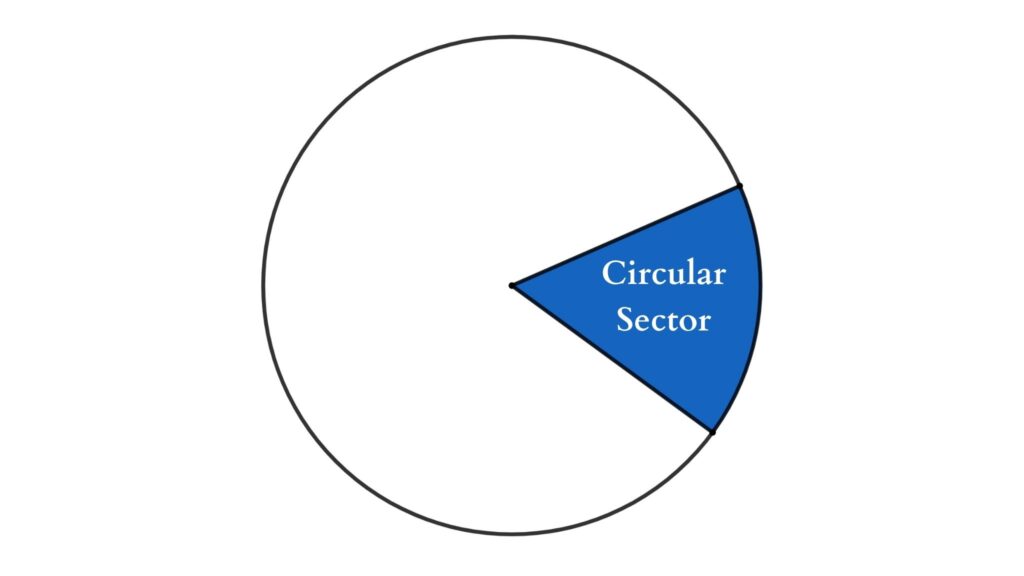
A sector is a closed figure bounded by an arc and two of its radii. Each sector has a unique central angle known as the sector angle. Read more
Segment
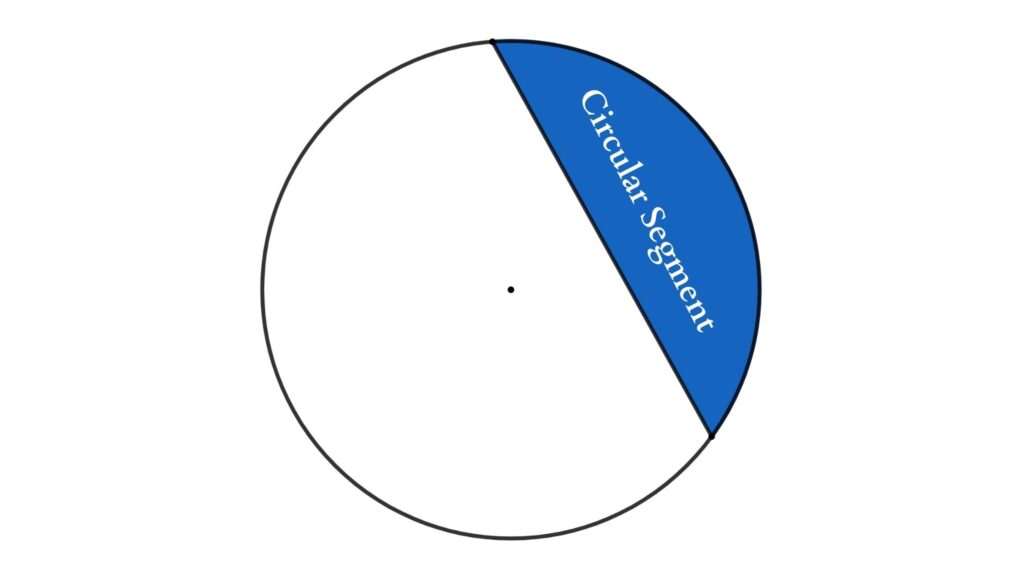
A segment is a region bounded by a chord and the corresponding arc. When we cut a circle through its chord, we get two segments. If the chord does not go through the center, we get a minor sector and a major sector. Read more
Arc
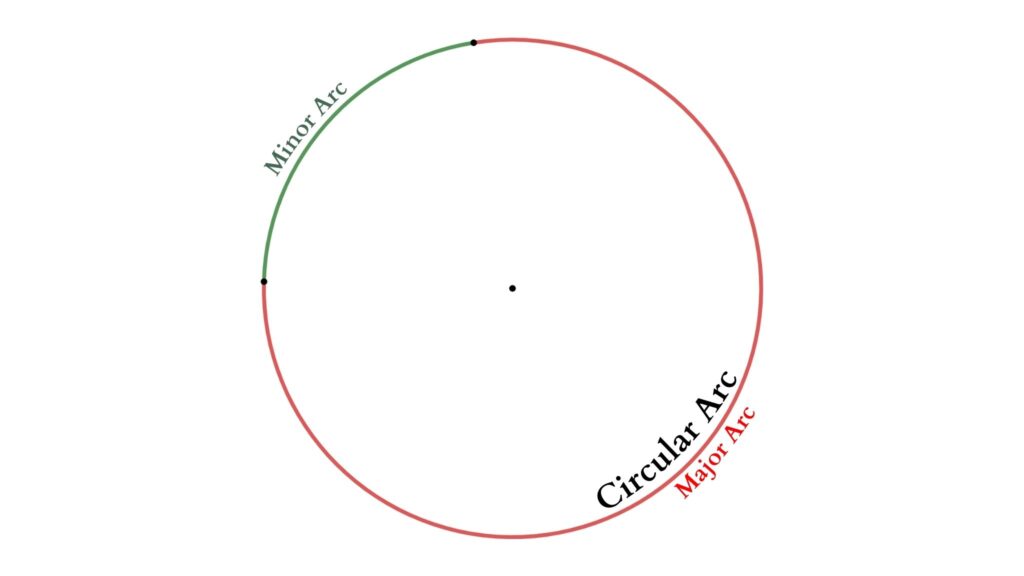
An arc is a portion of a circle obtained by cutting it at any two points. If the two points are not directly opposite, we will get a major arc and a minor arc.
Circumcircle and Incircle
The Circumcircle of a Polygon
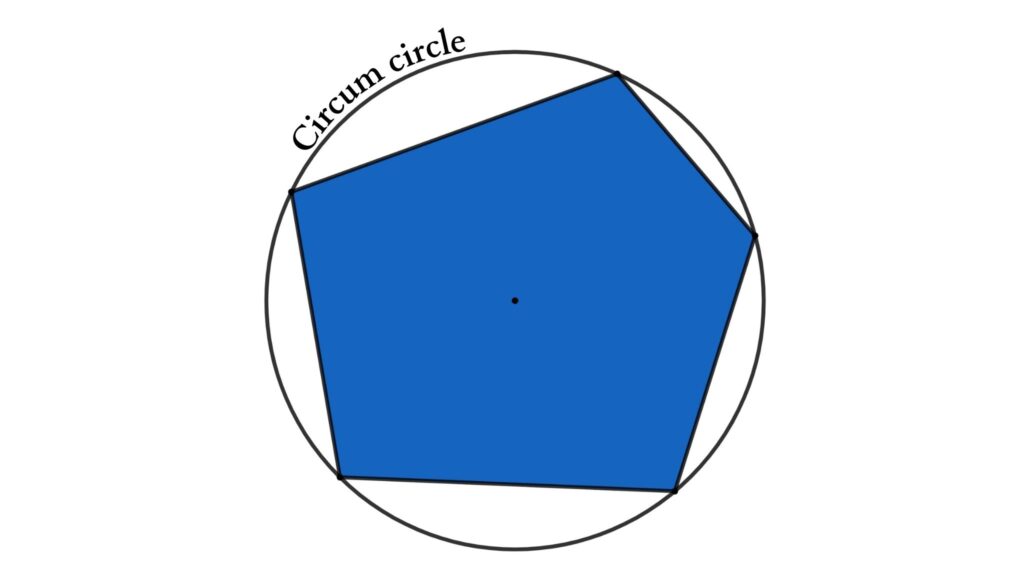
A polygon’s circumcircle is a circle that passes through all of the polygon’s vertices. The center of this circle is known as the circumcenter, and its radius is known as the Circumradius.
The Incircle of a Polygon
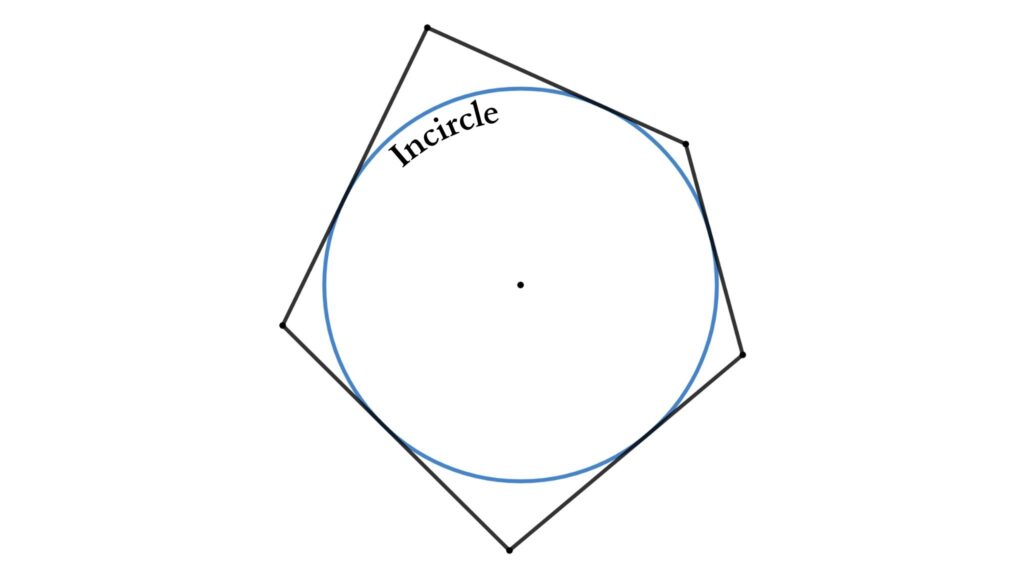
The incircle or inscribed circle of a polygon is the circle that will be contained within the polygon, and the sides of the polygon will touch the incircle (sides are tangential to the circle). The center of this circle is known as the incenter.

